Projects
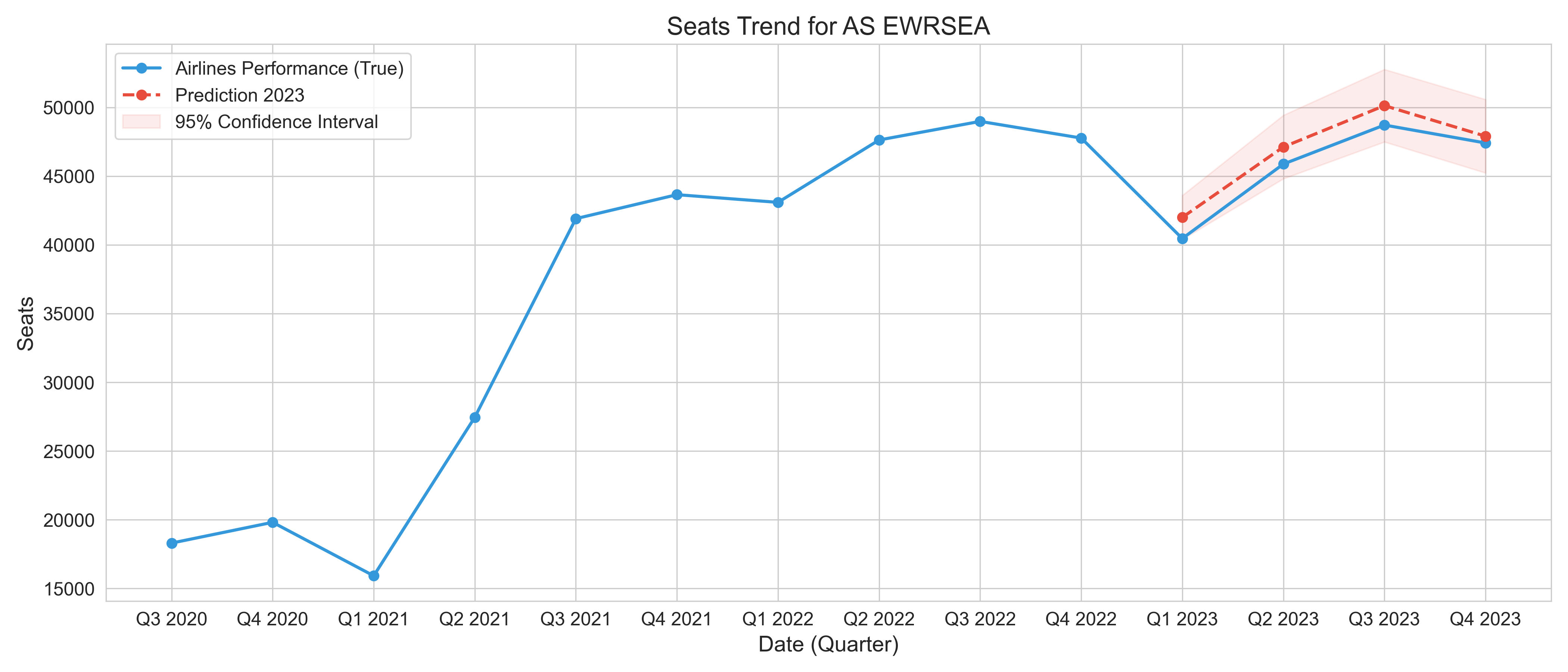
Airlines Seats Prediction and Competition Analysis
Project Time: Jun 2023 - Aug 2023
Location: Denver, CO
This project focuses on predicting the number of seats likely to be arranged for a given airline route in specified future quarters. The prediction model is built around Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), which have shown effectiveness in dealing with sequential data. The historical dataset used for training the model has been sourced from Diio Mi, which consists of details related to airline performance and future schedules. It also introduced the other economic data, demographics data, etc.
The recurrent neural network architecture in the model incorporates various features including embeddings for categorical features, bidirectional recurrent layers (either GRU or LSTM), a self-attention mechanism, feed-forward layers with optional dropout, batch normalization, and an output layer that can either predict an output directly or predict a mean and standard deviation, depending on the chosen loss function.
The initial architecture of the network is defined in the __init__ function. Categorical features are first transformed into embedding vectors via embedding layers. Then, based on the specified choice, either a GRU or LSTM layer is used as the recurrent component of the network. The recurrent layer output is transformed by a linear layer, then passed through a self-attention mechanism. This is followed by two feed-forward layers (fc1 and fc2) and batch normalization layers (bn1 and bn2).
During the forward propagation defined in forward(), the categorical features are embedded and concatenated with the continuous input features. This combined input is passed through the recurrent layer and transformed via a self-attention mechanism. If skip connections are enabled, the original output from the recurrent layer is added back to the attention-transformed output. The resultant output is passed through the feed-forward layers. Depending on whether MSE loss function is chosen, either an output value is directly predicted, or a mean and standard deviation are predicted.
The init_hidden
function is responsible for initializing the hidden states for the RNN layers. The dimensions of these hidden states are [num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, hidden_dim].
Overall, RNNNet offers a versatile RNN structure that supports various configurations and caters to a range of task requirements. Its functionality and adaptability make it a suitable choice for tasks involving sequential data with both categorical and continuous features.
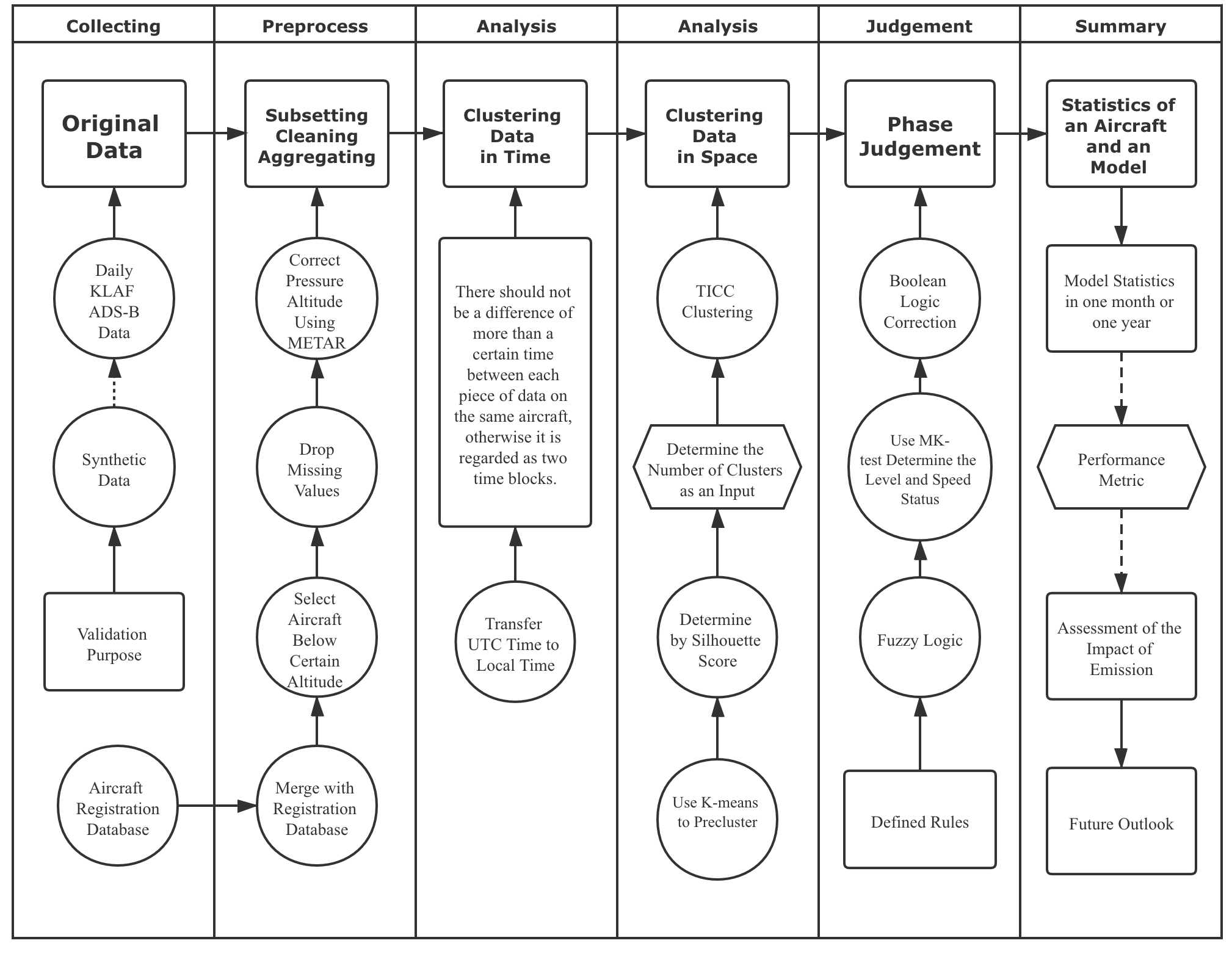
Advanced Flight Data Analysis and Phase Identification
Project Time: Sep 2020 - May 2024
Role: Project Lead
Location: West Lafayette, IN
The Advanced Flight Data Analysis and Phase Identification project is a pioneering initiative leveraging machine learning techniques and data preprocessing to address issues related to operational data analysis at general aviation airports. The project employs a novel algorithm to identify and classify different aircraft trajectories into flight phases. This approach improves classification performance by over 20%, allowing for more precise noise and emission modeling, ultimately helping address public concerns about airports.
The project focuses on the potential of Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) data, using machine learning to decode operational details from this data, leading to improved noise and emissions models. This process involves preprocessing flight records, incorporating meteorological data and other factors, to improve data accuracy and completeness. These efforts are particularly aimed at general aviation airports, which typically lack comprehensive operational data.
A core achievement of this project is the development of an algorithm that combines supervised and unsupervised machine learning techniques to classify aircraft trajectories into different flight phases. Compared to traditional methods, this approach significantly improves classification performance, demonstrating over a 20% enhancement in accuracy. This advancement is vital for better noise and emission modeling, directly addressing public concerns related to airports.
This research led to the successful creation of a framework capable of identifying different flight phases, solving significant problems faced in flight data mining. This new methodological approach was tested and validated using synthetic and empirical ADS-B data, and it showed promising results, positioning it as a feasible solution for deployment in airport operations. The identification of flight phases provides essential data for understanding aircraft operations and their environmental impact, enabling stakeholders to take meaningful action to reduce perceived environmental damage from noise and emissions.
Finally, the project lays groundwork for future research, proposing the development of a neural network structure that combines the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and Generative adversarial network (GAN). This network is designed to process sequential input data and generate missing flight maneuvering event records, reconstructing operational aircraft trajectories into a consecutively spaced data series. The ultimate goal is to develop a system that can provide real-time flight status data to airport managers, aiding in airport planning and facilitating accurate input into airport evaluation tools and environmental studies.
Enhancing Commuting with Optimized Vertiport Distribution and Demand Estimation
Project Time: Aug 2022 - Jan 2023
Role: Project Lead
Location: West Lafayette, IN
This project offered a dedicated analysis of the potential demand for Urban Air Mobility (UAM) operations, particularly concerning vertiport placement and the desired number of vertiports. The study explores the feasibility of UAM operations in Chicago, illustrating the time-saving benefits of eVTOL trips and providing a solid forecast for stakeholders about this emerging air transportation market. The results reveal UAM's competitive edge and potential to significantly enhance the transportation system's efficiency and equity.
Urban Air Mobility (UAM) concepts have obtained substantial attention in recent years due to their potential to offer an alternative mode of daily transport and alleviate issues such as traffic congestion and environmental pollution. This project, centered around UAM operations, carries out a dedicated analysis of the potential demand within a specific range, which is critical to determining the placement and optimal number of vertiports. The focus of this investigation was the Chicago metropolitan area, a densely populated urban region considered an ideal candidate for such novel air transportation services.
By assessing the commuting demand in Chicago, the research provides valuable insights into the feasibility of UAM operations and vertiports distribution. The study applies techniques that quantify the benefits brought by UAM, with a particular focus on the time-saving advantages of eVTOL trips compared to traditional driving commutes. The results highlight how competitive the UAM network can be, thereby aiding UAM stakeholders in understanding the prospective market for this innovative transportation modality.
Additionally, the research underscores the necessity for more comprehensive market evaluations, including more subjective surveys, alongside the objective census data utilized. Collecting additional opinions from policymakers, surrounding communities, and operators are advised, to ensure that benefits for both users and non-users are considered.
The project also identifies the need for an optimization program to examine vertiport placement more closely and the introduction of a critical constraint, such as vertiport capacity, into the design of this new transportation system. Ultimately, this project argues that UAM should demonstrate the benefits it can bring to the public and promote an efficient and equitable transportation system that provides a convenient and affordable form of transportation for each trip. The study's findings offer a robust forecast for UAM stakeholders and a foundation for future research and developments in this emerging field.

Pilot Performance Analyses and Training Evaluation for Inflight Safety
Project Time: May 2022 - Aug 2022
Role: Project Lead
Location: West Lafayette, IN
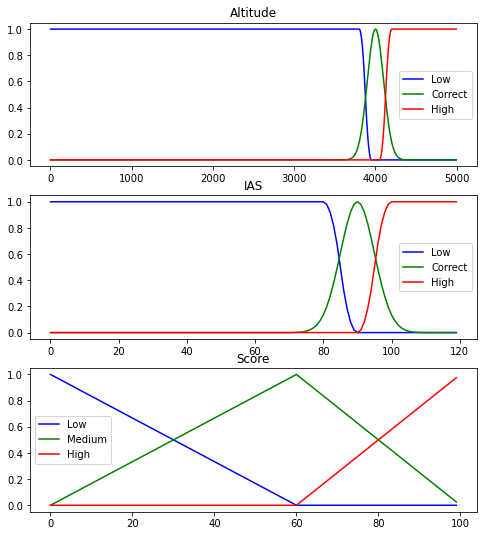
This project centered on investigating Loss of Control In-flight (LOC-I) accidents with the aim of devising ways to mitigate future occurrences. The project has identified energy management as a key factor in LOC-I incidents and is now focused on developing a suite of maneuvers training that could potentially be included in pilot training to prevent LOC-I. Experimental data collection will be used, with pilots divided into control and experimental groups, each receiving different energy management training. This data will be analyzed using CloudAhoy and fuzzy logic to evaluate the pilots' performance and the effectiveness of the training interventions.
The project's primary purpose is to study LOC-I accidents, which are a significant concern in aviation safety. LOC-I accidents, often resulting from a pilot’s inability to accurately assess, comprehend, and control the energy state of the aircraft, are typically fatal. Through a comprehensive meta-analysis of reported LOC-I accidents, the researchers identified energy management as a pivotal factor in these occurrences.
The project involves analyzing different training maneuvers to determine if it's possible to devise a specific maneuver or a suite of maneuver training to mitigate LOC-I. This initiative is aimed at enhancing pilots' understanding and control over the energy state of their aircraft. The pilots were divided into three groups: one control group and three experimental groups. The three experimental groups will receive distinct interventions in terms of energy management training. The post-test flight, similar to the pre-test, will help determine whether the training interventions had any statistically significant impact on the energy management capability of the groups.
To evaluate pilot performance, fuzzy logic is applied, offering a degree of correctness compared to the instructions, thus determining how close the current status is to the desired one. The report notes that the training might help improve the lower limit of performance but may not have a significant impact on the upper limit.
Lastly, the project's report discusses the impacts of different training videos on the pilot groups, noting improvements in some and lesser changes in others. The report also acknowledges limitations due to the limited sample size and notes that many factors, such as pilot interactions or additional research by the pilots, could have immeasurable effects on the experiment.
Advanced Image Processing and Optimization Solutions in AI Applications
Project Time: Jan 2022 - May 2022
Location: West Lafayette, IN
Designed object classification, detection and localization models using convolutional and skip block networks, as well as independently implemented YOLO architecture, achieving accurate results on the COCO dataset. Additionally, generated realistic images with GANs using the CelebA dataset.
The goal of the first project is to understand the usage of YOLO algorithm. The full name for YOLO is You Only Look Once. It is useful for detecting and localizing for multi-instance object. It improves detection accuracy and speed compared to traditional detection schemes. It treats object detection as one regression problem, so it is also called a one-stage algorithm. The image is divided into a grid of cells and the job of predicting the bounding-box and the class-label for an object in the image is the responsibility of the grid cell that has the center of the object in it. The project used YOLO to apply in the COCO images.
The goal of the second project is to understand the usage of generative adversarial network (GAN). GANs are a framework for teaching a DL model to capture the training data’s distribution so model can generate new data from that same distribution. They are made of two distinct models, a generator and a discriminator. Particularly, generator code will use Transpose Convolutions to expand noise vectors into images that will look very similar to the images in the training data. The project used CelebFaces Attributes Dataset that contains thousands of celebrity images. The expected objective of the project is to produce images will look very similar to the training images without being exactly the same as any of them.

Study on the Solution of Traveller Salesman Problem with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Project Time: Jan 2021 - May 2021
Location: West Lafayette, IN
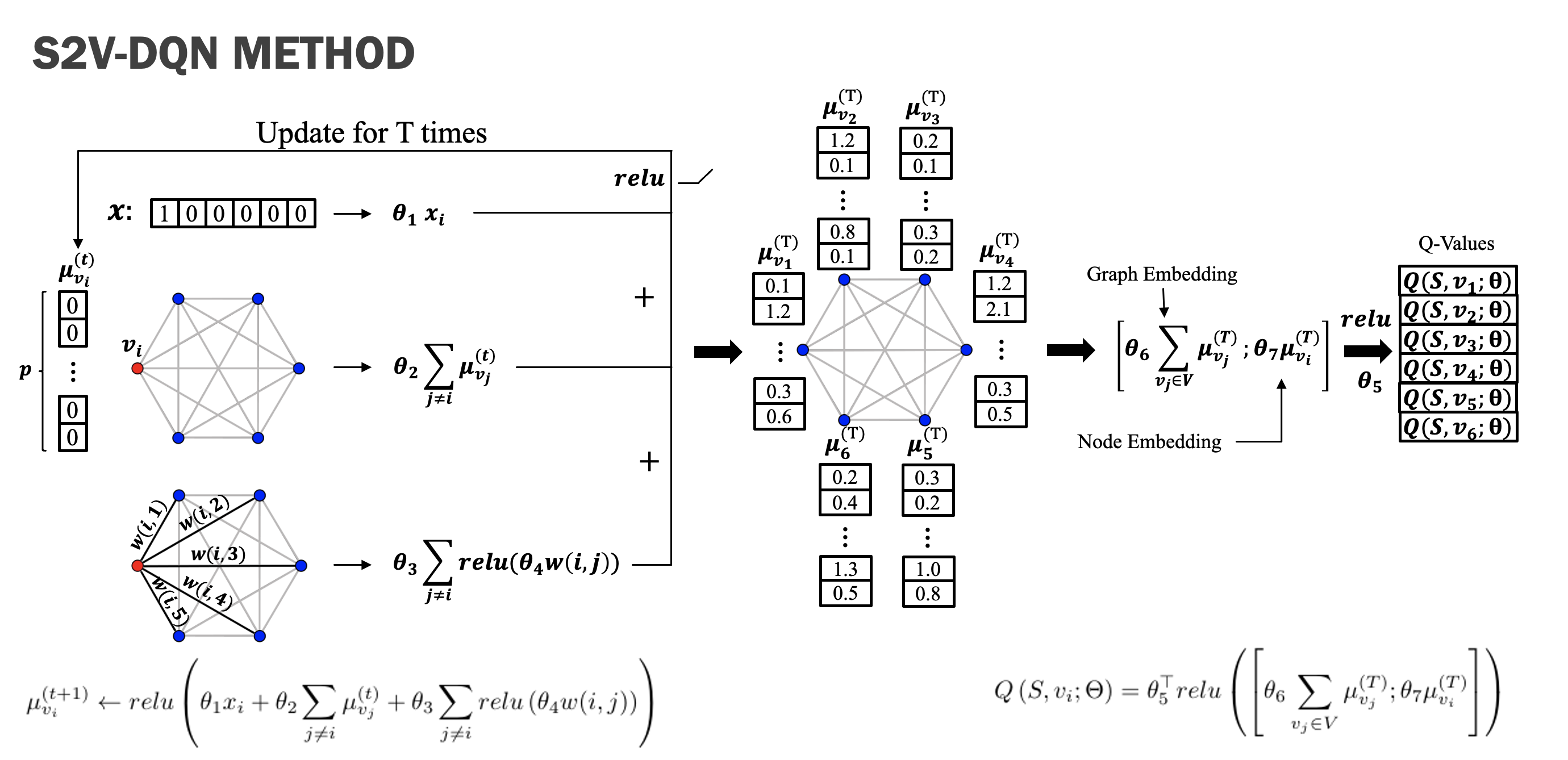
Working with my teammate Site Bai, Deep Reinforcement Learning was applied to solve the Traveler Salesman Problem and two TSP variants with constraints. Firstly, we identified S2V-DQN as the state-of-the-art Deep RL algorithms that combines Graph Neural Networks to solve the TSP, re-implemented it in PyTorch and achieved identical results reported in the original paper. Secondly, we apply S2V-DQN to solve the TSP with Time Windows and achieved comparable results with other operations research tools. Thirdly, we test the performance of S2V-DQN on the TSP with Pickup and Delivery, and the results are unsatisfying. We analyze the reason may be that the brute-force masking scheme on the output layer is not enough for com- plex constraints, which may need elaborate design to be intrinsically embedded into the deep networks.
In this project, we studied how to apply Deep Reinforcement Learning to solve the Traveler Salesman Problem. Specifically, we identified S2V-DQN as the state-of-the- art Deep RL algorithms that combines Graph Neural Networks to solve the problem, re-implemented it in PyTorch and achieved identical results reported in the original paper. Moreover, we applied S2V-DQN to solve the TSP with simple constraints like TSP with Time Windows and found it effective regarding problem of this kind. We also explored the performance of S2V-DQN on the TSP with more complex constraints like the TSP with Pickup and Delivery, and reported unsatisfying results. We analyzed that the cause may be imposing the brute-force masking scheme on the output layer while the problem itself may need elaborate design of the deep networks that can intrinsically embed the constraints. This points out the future direction of this work and many other on-going works are also good references.
Bike-sharing system demand factors analysis and prediction
Project Time: Aug 2020 - Dec 2020
Role: Project Lead
Location: West Lafayette, IN
In this project, we are proposing to perform statistical analysis on the data set “SeoulBikeData.csv”. The data set we have used includes weather information (temperature, humidity, wind speed, visibility, dew point, solar radiation, snowfall, rainfall), the number of bicycles rented per hour, and date information. This paper will discuss the different kinds of usable models for the purpose of hourly rental bicycle demand forecasting.
Many cities are now offering bike-sharing systems to improve the mobility and comfort of their residents. The system has been recently developed and provides people with the shared use of bicycles. The bicycle system offers users rentable bicycles from a docking station that can be ridden and returned at other docking stations. Bicycle sharing systems began in 1965 in Amsterdam, Netherlands and have been used worldwide since 2000 over the past twenty years. It is important to make these rental bikes available and accessible to the public at the right times in order to lessen the downtime. Eventually, providing a city with a stable supply of rental bikes could become a major concern. Many countries have bike-sharing systems, such as Ddareungi, a South Korean bike-sharing system that started in 2015 (Seoul bike). With the great advances in transportation systems and information technology, the use of rental bikes is increasing day by day in Seoul. Therefore, there is a need to manage the supply of bicycles to accommodate the the demand in order to provide continuous and convenient services to users.
Imaginary Surface Integration and Airspace Design for eVTOL Operation Safety
Project Time: Aug 2019 - May 2020
Role: Project Lead
Location: Berkeley, CA
Project designed a comprehensive vertiport safety envelope for Urban Air Mobility (UAM) and optimized its urban airspace for efficient and safe operation of electric Vertical Take-off and Landing (eVTOL) aircraft. It also created a cutting-edge simulation model that determined the most efficient eVTOL routes while taking into account both urban airspace and ATC limitations, improving safety and operational efficiency.
Local and Transfer Passenger Composition Patterns Analysis
Project Time: May 2024 - Aug 2024
Location: West Lafayette, IN
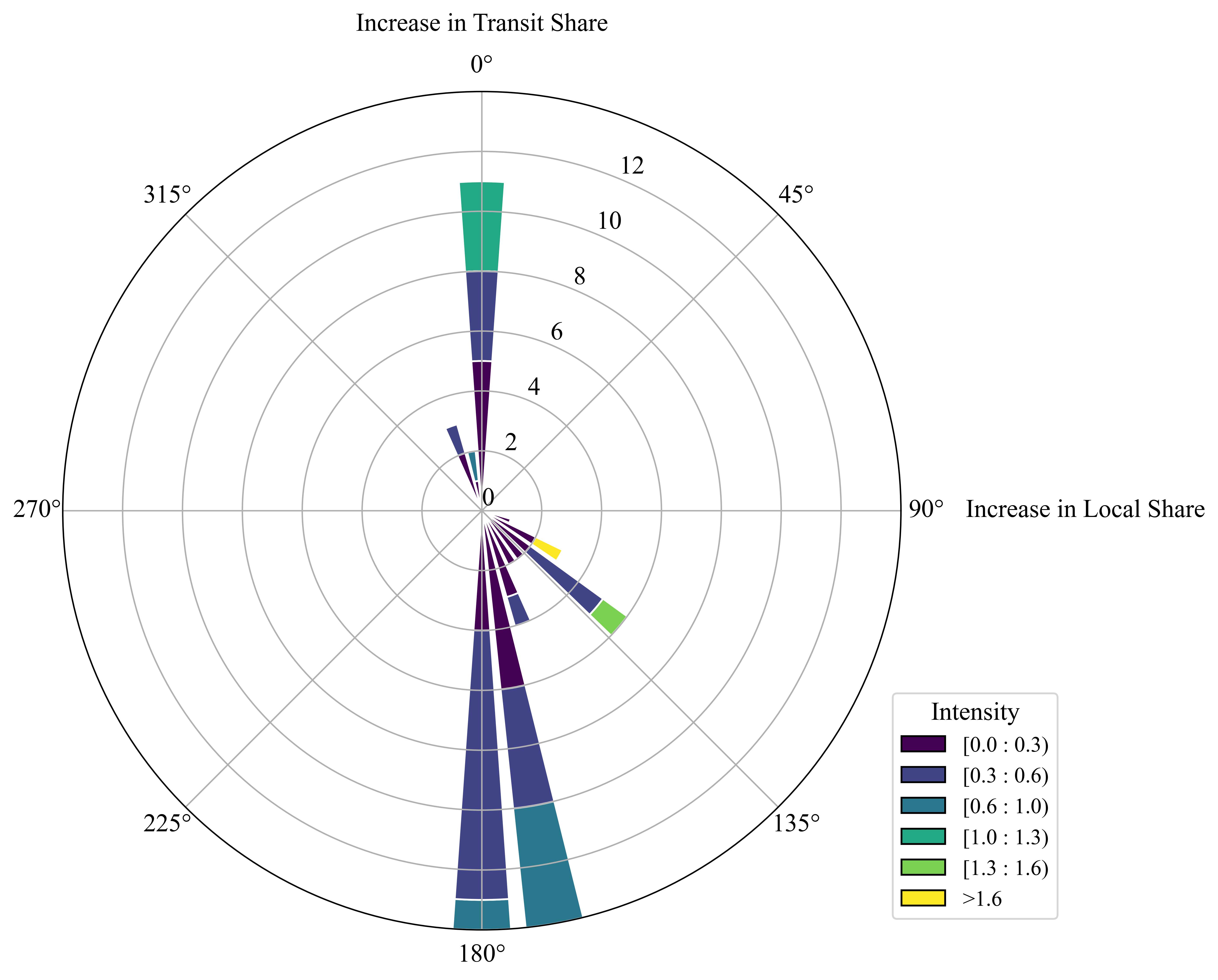
Local passenger and transfer passengers have different behaviors, services needed, and impact during air travel. Understanding the dynamics of composition of local passengers and transfer passengers is crucial for airline competitions and airport operations. In this study, we focus on reveling the insights into the composition of local passengers and transfer passengers from various dimensions. Based on our research ...
Understanding the local share is pivotal for enhancing both passenger experience and airport revenue.
Other Projects
- Behavior Modeling for Autonomous Vehicles